Can You Compost Apple Cores?
Apples (and dried apple chips) are a core snack in our house. As a family who composts in a variety of ways, I get questions like “Can you compost apple cores?” and “Can you compost apple seeds?” Read on for more details on composting apple cores and how they impact your compost pile.
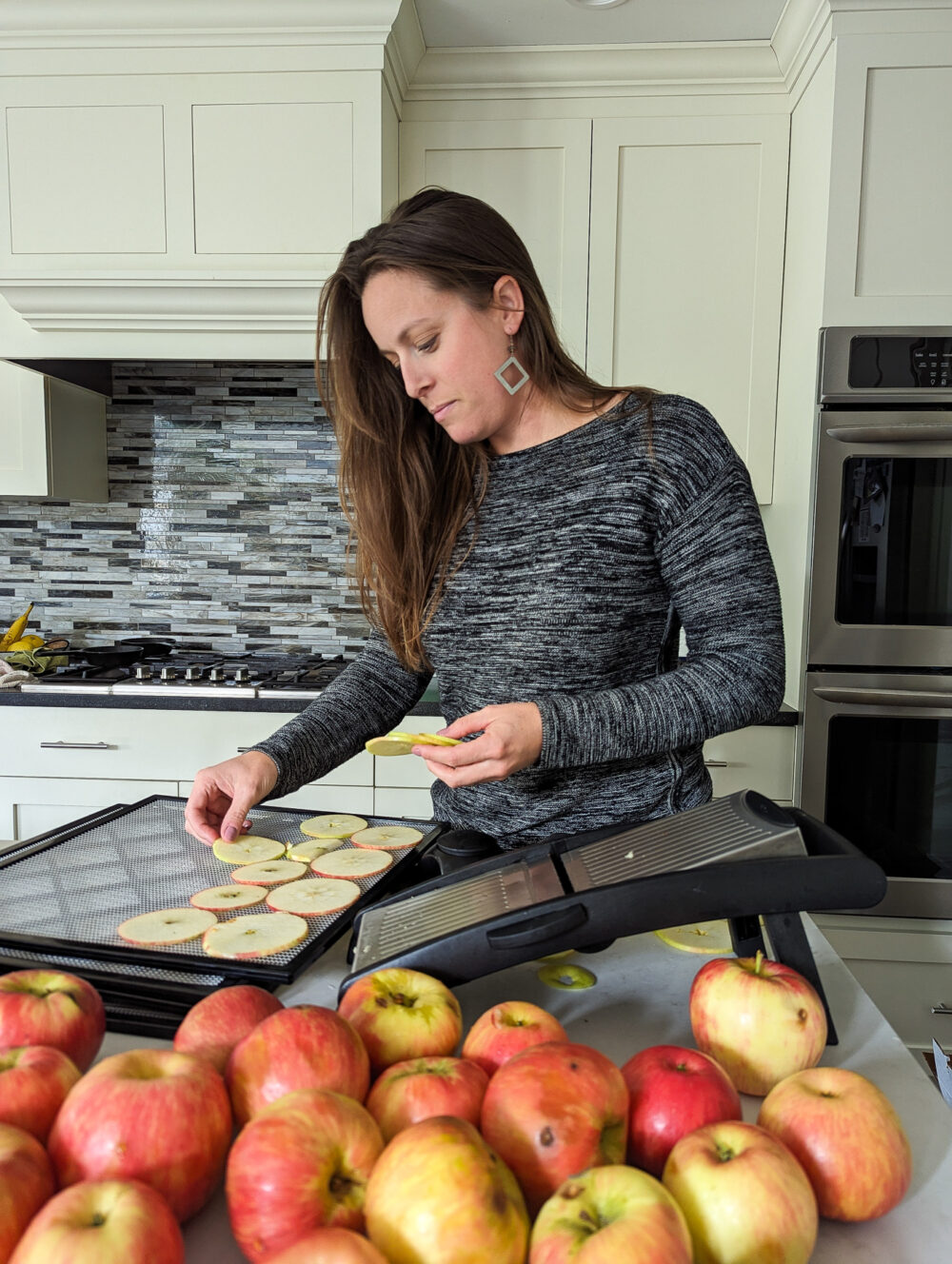

We eat a lot of apples in our house. Admittedly, we are partial to Honeycrisp. Can you blame us? My son is a huge fan of these homemade dried apple chips. And we occasionally make this apple pie from my husband’s grandmother and my grandmother’s homemade applesauce. So when apples are in season at our local farm or orchard, I buy “seconds” apples in bulk and use them to make a ton of dried apple chips.
If you’re not familiar with “seconds” apples, they’re the apples that are totally nutritious and safe to eat but aren’t quite pretty enough to be put on grocery store shelves or farmers’ market baskets. They have a spot or a nick on them or might be too big or too small to fit into a perfect bushel of apples.
It’s really an indication of our odd standards around food aesthetics, but that’s a story for another day. In this case, it means I get more delicious apples for a much lower cost than I would pay at a traditional grocery store. It means less food waste, more profit for the orchard or farm, and money saved for me. Win-win-win.
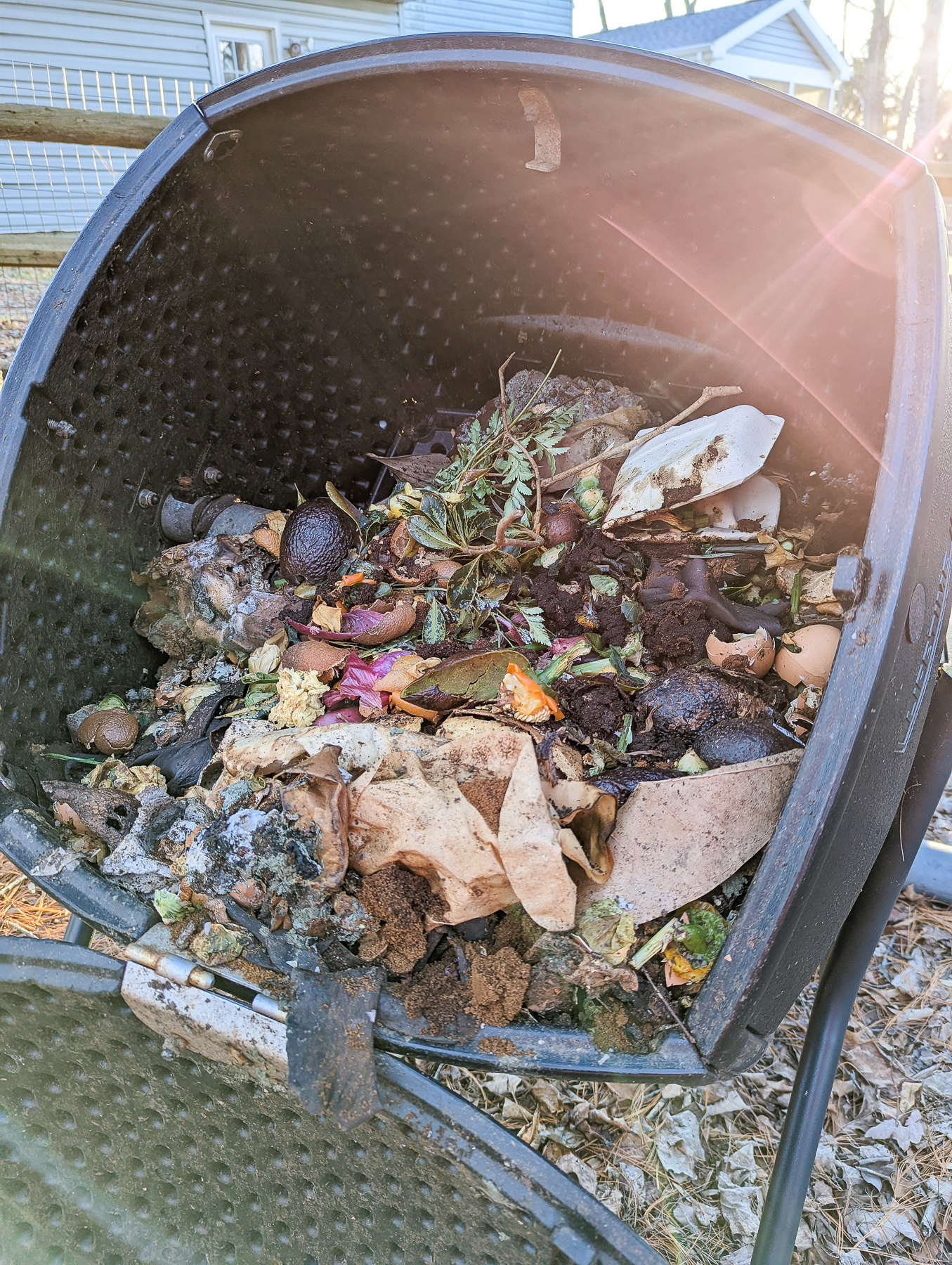
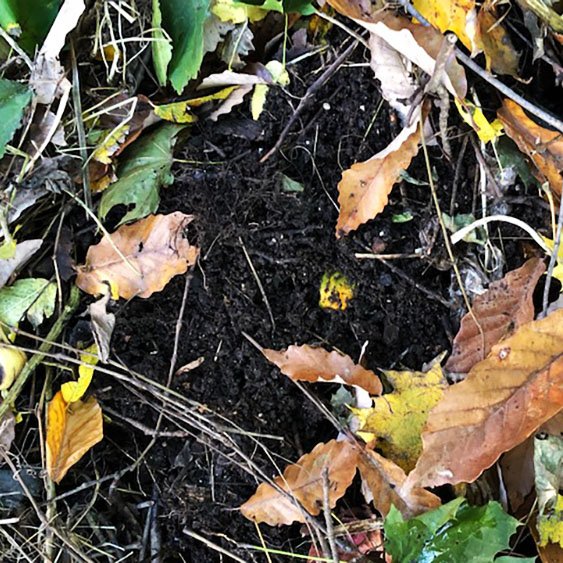
We keep the skins on the apples to make apple chips, but we still have a bunch of odds and ends left from the apples that we don’t use. I certainly don’t want to throw them in the trash, because they’ll just hang out in the landfill for ages releasing methane. So what to do with them? How about we toss those apple cores into the compost bin? Can you compost apples?

Can you compost apple cores?
Let’s get to the core of the question, shall we not? You can definitely compost apple cores, including the seeds. There are some varying views on composting apple seeds, but if you’re just looking to reduce your food waste and create some soil amendment for your home garden, go ahead and toss the whole apple core in the compost heap. You’ll be just fine!
Apple cores are organic material that breaks down relatively quickly. Adding apple cores to your compost pile contributes essential nutrients and helps reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills. For more guidance on what items are compostable, check out this resource on Can I Compost…? from our comprehensive Guide to Composting at Home.
When composting apple cores, it is helpful to cut them into small pieces to speed up the decomposition process. By observing the basic principles of composting and incorporating apple cores with other compostable materials, you can create nutrient-rich, beneficial compost for your garden and contribute to a sustainable environment.

Apples in the Compost Pile
Composting is a natural process in which organic matter breaks down into a nutrient-rich, soil-like substance called compost. This process is facilitated by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi, which decompose the organic material, turning it into a valuable amendment for gardens and landscapes. Composting not only reduces the amount of food waste and yard waste that ends up in landfills but also contributes to a healthier environment by enhancing the quality of soil and supporting plant growth.
In a composting bin or pile, the decomposition of organic materials occurs through the activities of various microorganisms. These bacteria and fungi consume the organic matter, breaking it down into simpler compounds, and releasing nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium into the compost. This nutrient-rich mixture greatly benefits plants when added to garden soil, as it improves soil structure, enhances water retention, and provides essential nutrients for plant growth.
Apple cores, being rich in nitrogen and containing minerals like calcium and potassium, make a valuable contribution to compost piles. As a “green” material, they decompose quickly—taking around two months to break down completely—adding to the variety and balance of components in compost.
It is essential to maintain a proper balance of “green” materials, such as apple cores and other food waste (like banana peels, coffee grounds, and vegetable peels), with “brown” compost materials, like cardboard, paper, and yard waste, to create an effective and healthy compost pile. A well-balanced compost system promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms that work efficiently to decompose organic materials, producing a valuable resource for enhancing the health of plants and soil.
Related Reading: What Is The Right Ratio of Greens and Browns For Composting At Home?
Composting apple cores is a beneficial practice that can improve soil quality, reduce landfill waste, and support a sustainable environment. When managed properly, the composting process transforms organic waste materials into a valuable resource that contributes to the health and productivity of garden plants and the surrounding ecosystem.

Composting Methods
Apples and apple cores can be composted using various methods, each with its own advantages and procedures. By incorporating these methods into your composting routine, you can reduce waste and create nutrient-rich compost for your garden.
Cold Composting is a simple and low-maintenance process that involves compiling organic matter into a pile or a compost bin. Apples can be added to the cold compost, but it is essential to maintain a balanced mix of green and brown materials. Layering other organic materials like dried leaves, grass clippings, and small branches with apple cores and other “green” materials will enhance the decomposition process. Cold composting might take longer than other methods, but it’s an excellent solution for those who prefer a hassle-free approach.
Hot Composting is ideal for those who desire a faster decomposition process. Incorporate apples into a compost pile that is turned and aerated regularly, which ensures it reaches optimal temperatures. Microorganisms break down the materials, including apple cores, in just a few weeks when temperatures remain hot (an indication that the microorganisms are in an ideal environment for processing all the organic waste and working hard to get through the pile). Remember to maintain a balanced ratio of green to brown materials and monitor the pile’s moisture content to promote successful hot composting.
Vermicomposting utilizes earthworms, specifically red wigglers, to process organic matter like apple cores into vermicompost. Add apple peels and cores to the worm bin, but be sure not to overload the system as it might attract unwanted pests. Worms will consume the apples and excrete nutrient-rich worm castings, which are an excellent natural fertilizer for plants.
Anaerobic composting is another method that can be used to compost apple cores. Bokashi composting is a common style of anaerobic composting used at home. Anaerobic composting involves organic materials breaking down in the absence of oxygen, usually in a closed container. Although this method may result in undesirable smells if not properly managed, it can be useful in situations where outdoor space is limited or composting needs to be contained.
By composting apple cores, individuals can reduce their waste output and create a soil amendment that is both environmentally friendly and beneficial for plant growth. By following best practices and maintaining a balanced compost pile, the end result will be a nutrient-rich, organic material that can be used to sustain healthy and edible plants in any garden.

Frequently Asked Questions
Can apple cores go in a compost bin?
Yes, apple cores can be composted and added to a compost bin. They are considered organic material and can break down in a compost pile or bin. Apple cores are categorized as “green material” and can decompose quickly, contributing to the nutrient content of the compost.
How to compost fruits and vegetables properly?
To compost fruits and vegetables properly, follow these steps:
- Create a balance between “green” materials (such as fruit and vegetable scraps) and “brown” materials (such as dried leaves, straw, and small branches). Aim for a ratio of about 2 parts brown to 1 part green as a general guideline, though this may vary based on what types of greens and browns you add and the conditions of the compost pile.
- Chop up larger fruit and vegetable scraps to speed up the decomposition process.
- Turn the compost pile periodically, which helps to aerate the material and promote aerobic decomposition.
- Keep the pile moist, but not soggy. The moisture content should be like a damp sponge.
- Monitor the temperature of the compost pile. It should heat up as microorganisms break down the organic matter. If it doesn’t, try adding more green material or turning the pile more frequently.
Are rotten apples safe for composting?
Yes, rotten apples and old apple cores are safe for composting. They can be added to your compost pile along with other fruit scraps and vegetable trimmings. Even whole apples can go into the compost heap if no part is salvageable for eating.
Hopefully, you don’t have too many apples that go bad, but you may have a fair amount of rotten apples if you have an apple tree or two in your yard and homegrown apples fall to the ground before they are ready for harvesting.
Whole apples may take a long time to break down in a regular compost pile, so you might want to cut the apples into small chunks before composting apples. But it’s definitely not required.
As they decompose, they will contribute to the nutrient content of the compost. However, avoid adding diseased material to the compost pile, as it may introduce pathogens that could harm your plants.
Can you compost apple seeds?
While apple seeds can technically be composted, they may not break down as quickly as the rest of the apple core. Additionally, apple seeds contain trace amounts of a substance called amygdalin, which can release cyanide when broken down. The risk is minimal, so some people remove the seeds before adding apple cores to your compost pile. But I just toss the whole core in the pile and haven’t had any issues to date.
How long does it take to compost an apple core?
It takes about 2 months for an apple core to decompose in a compost pile or bin. The exact time may vary depending on factors such as the size of the apple core, the balance of green and brown materials in your compost, and the conditions of the compost pile (temperature, moisture, and aeration).

If you like this post about composting apple cores, you might also like
Do You Need to Water Your Compost Pile?
8 Simple Tips to Manage a Countertop Compost Bin in the Summer

Jen Panaro
Jen Panaro, founder and editor-in-chief of Honestly Modern, is a self-proclaimed composting nerd and advocate for sustainable living for modern families. To find her latest work, subscribe to her newsletter, Stepping Stones.
In her spare time, she’s a serial library book borrower, a messy gardener, and a mom of two boys who spends a lot of time in hockey rinks and on baseball fields.
You can find more of her work at Raising Global Kidizens, an online space to help parents and caregivers raise the next generation of responsible global citizens.